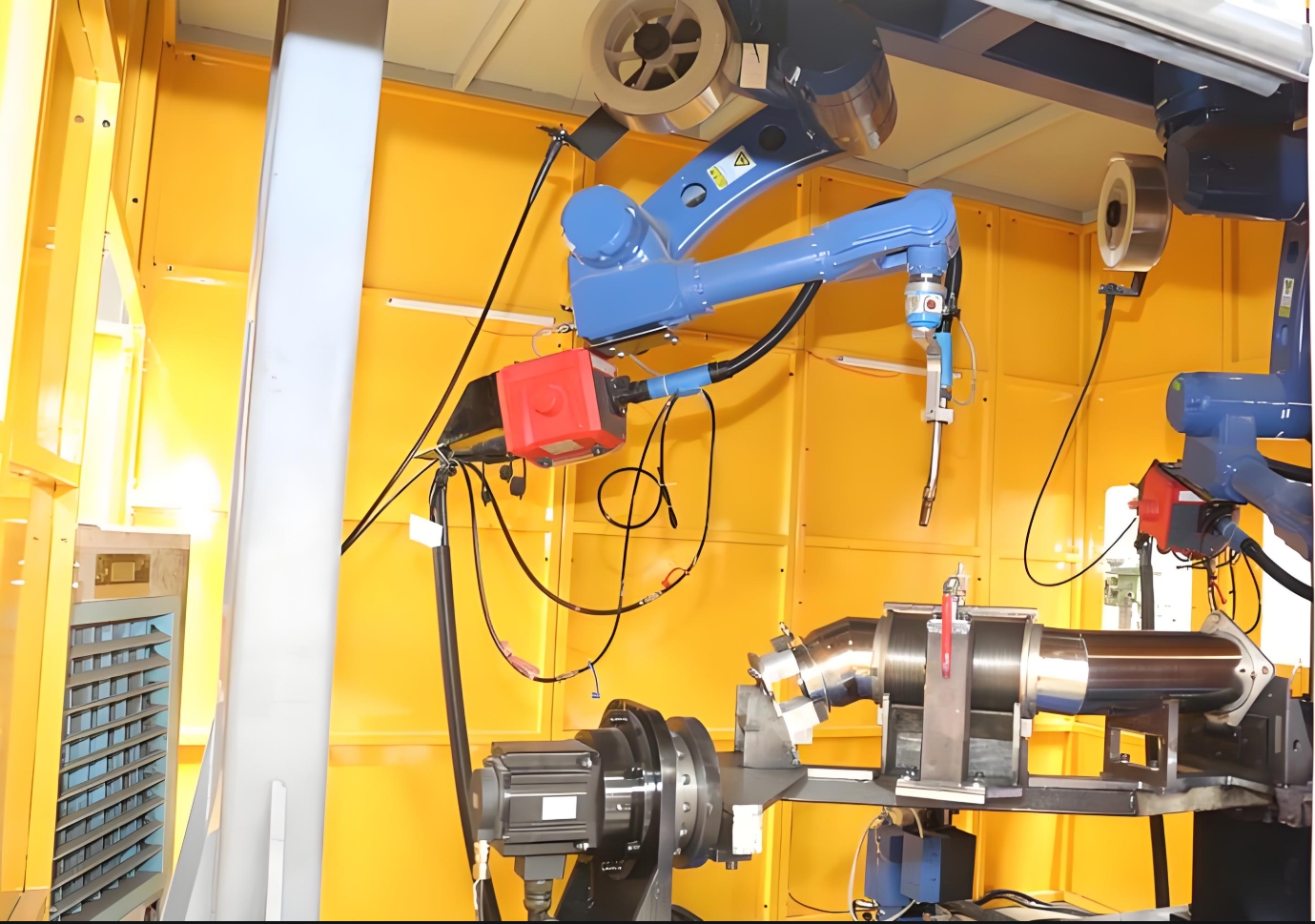
The automotive industry is synonymous with innovation, demanding relentless precision, speed, and reliability in component manufacturing. Among critical automotive parts, exhaust systems—particularly exhaust pipes—play a pivotal role in vehicle performance, emissions control, and noise reduction. As manufacturers strive to meet stringent quality standards and production targets, welding robots have emerged as indispensable tools in the fabrication of exhaust systems. This article explores how robotic welding systems, integrated with advanced positioning equipment like rotary tilt positioners and customized fixtures, are revolutionizing the production of automotive exhaust pipes, elevating efficiency, consistency, and product quality to unprecedented levels.
1. The Complexity of Exhaust Pipe Manufacturing
Exhaust pipes are subjected to extreme conditions, including high temperatures, corrosive gases, and mechanical vibrations. To withstand these challenges, they are typically fabricated from stainless steel or aluminized steel and require seamless, airtight welds across complex geometries. Traditional manual welding processes often struggle to maintain consistency in such applications, leading to defects like porosity, incomplete fusion, or distortion.
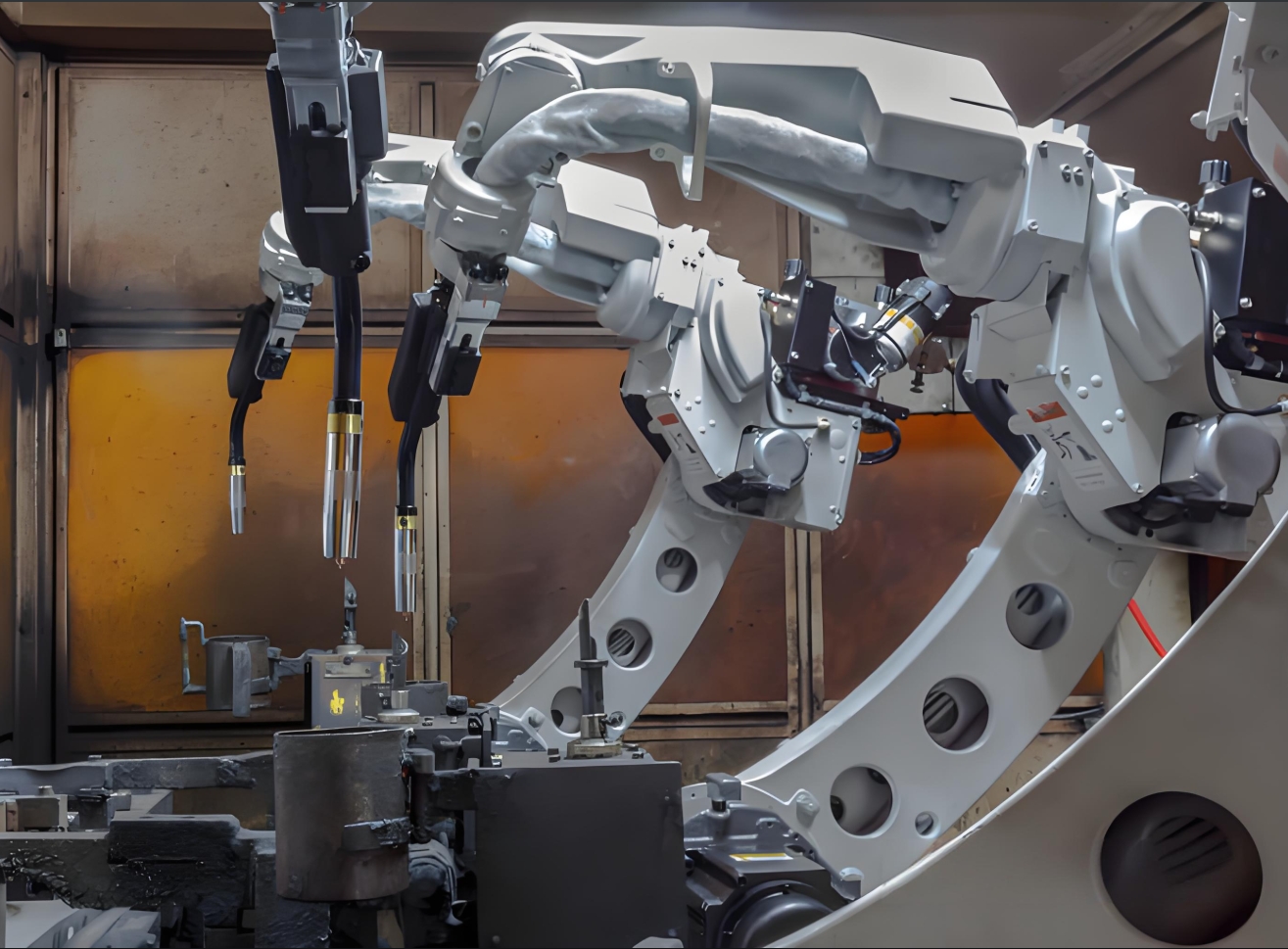
Welding robots, however, excel in handling these complexities. Equipped with multi-axis articulation and synchronized with precision positioning systems, they deliver flawless welds on curved surfaces, flanges, and joints—critical for ensuring exhaust system integrity.
2. Robotic Welding in Action: Key Applications for Exhaust Pipes
2.1 Tube-to-Flange and Tube-to-Muffler Welding
Exhaust systems comprise multiple components, including pipes, catalytic converters, resonators, and mufflers. Robotic welding systems automate the joining of tubes to flanges or muffler housings, ensuring uniform penetration and minimizing heat-affected zones (HAZ). For example, a 6-axis articulated robot can maneuver around a pipe’s circumference, maintaining optimal torch angles and travel speeds even on contoured surfaces.
2.2 Laser Welding for Thin-Walled Components
Modern exhaust pipes often feature thin-walled designs to reduce weight while maintaining strength. Laser welding robots, with their high energy density and narrow weld seams, prevent warping and preserve material properties. This is particularly advantageous for stainless steel exhaust systems, where precision is paramount.
2.3 Multi-Pass Welding for Thick Joints
For heavy-duty exhaust systems in commercial vehicles, robotic gas metal arc welding (GMAW) systems execute multi-pass welds to build up robust joints between thick-walled pipes and brackets. Adaptive welding algorithms adjust parameters in real time to accommodate material variations.
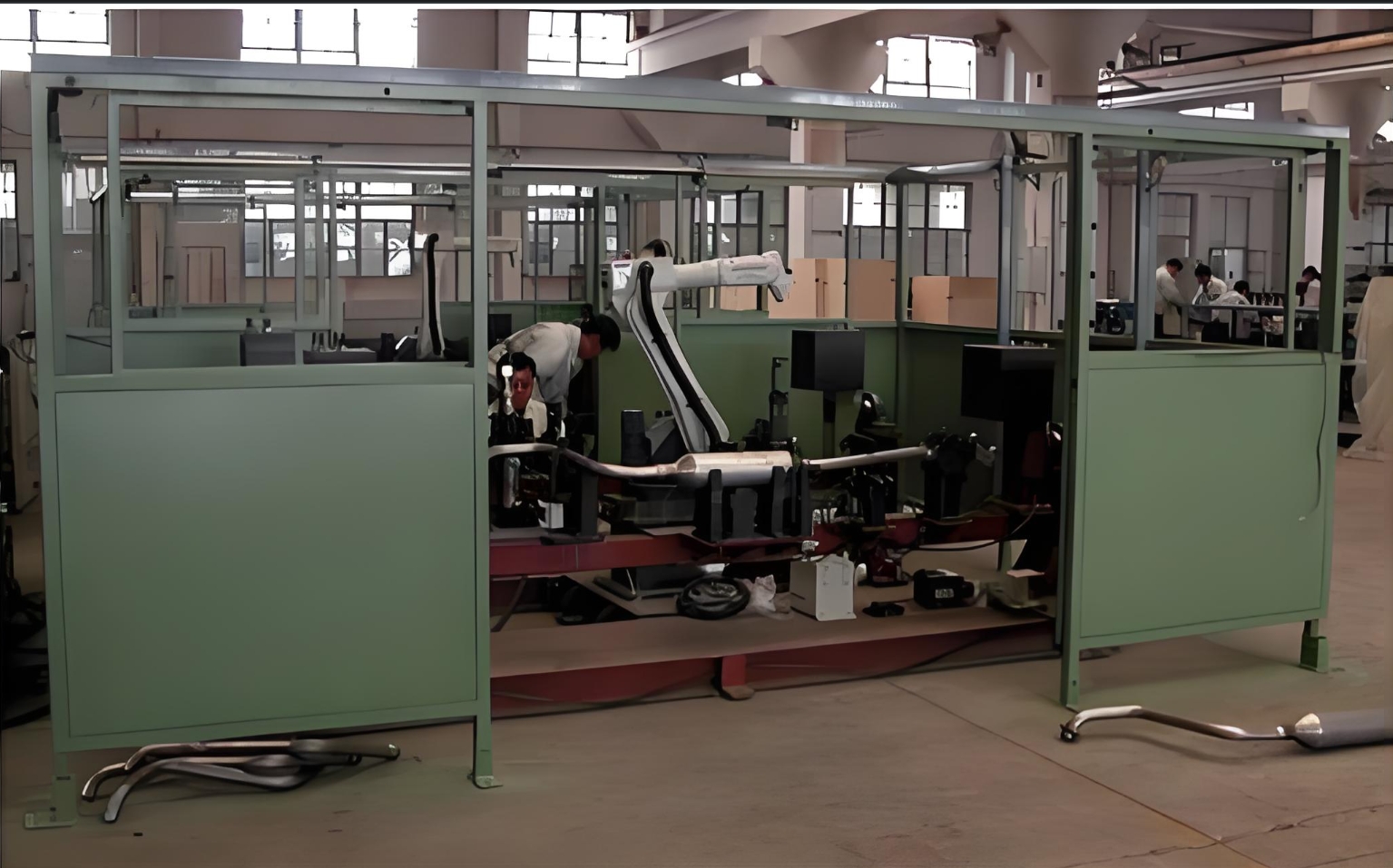
3. Enhancing Flexibility with Rotary Tilt Positioners
A robotic welding cell’s efficiency hinges on seamless coordination between the robot and workpiece. Rotary tilt positioners are pivotal in this process, enabling 360-degree rotation and tilting of exhaust pipes during welding. Benefits include:
- Optimal Joint Accessibility: The positioner reorients the pipe to present the weld seam in the flat or horizontal position, simplifying robot programming and reducing cycle times.
- Reduced Repositioning: By dynamically adjusting the workpiece, the robot can complete multiple welds in a single setup, minimizing idle time.
- Improved Ergonomics: Operators load/unload components while the robot welds, maximizing throughput.
For instance, a dual-station positioner allows one pipe to be welded while the next is loaded, achieving near-continuous production.
4. Precision Fixturing: The Backbone of Consistency
Customized welding fixtures are critical for holding exhaust components in exact alignment during robotic welding. Key design considerations include:
- Clamping Mechanisms: Pneumatic or hydraulic clamps secure pipes, flanges, and brackets without marring surfaces.
- Modularity: Quick-change fixtures accommodate varying pipe diameters or configurations, ideal for mixed-model production.
- Thermal Management: Fixtures made from heat-resistant materials withstand prolonged exposure to welding arcs.
Advanced fixtures integrate sensors to verify component placement before welding commences, eliminating misalignment defects.
5. Quantifying Efficiency Gains
The adoption of robotic welding systems in exhaust pipe manufacturing delivers measurable improvements:
- Cycle Time Reduction: A robotic MIG welder can complete a circumferential weld in 60 seconds, compared to 180+ seconds for manual welding.
- Higher Uptime: Robots operate 24/7 with minimal downtime, boosting annual output by 30–50%.
- Material Savings: Precise parameter control reduces spatter and rework, lowering consumable costs by 15–20%.
For example, a Tier-1 automotive supplier reported a 40% increase in throughput after deploying robotic cells with synchronized positioners for exhaust assembly.
6. Elevating Quality to Automotive Standards
Robotic welding ensures compliance with automotive quality benchmarks such as IATF 16949:
- Repeatability: Robots replicate weld paths with ±0.1 mm accuracy, eliminating human variability.
- Defect Detection: Integrated vision systems or arc monitoring sensors detect irregularities mid-process, triggering immediate corrections.
- Documentation: Automated systems generate traceable weld logs, critical for audits and recalls.
Post-weld inspections reveal that robotic systems reduce porosity and crack rates by over 90% compared to manual methods.
7. Sustainability and Future Trends
Automotive manufacturers are increasingly prioritizing sustainability. Robotic welding supports this shift by:
- Reducing Energy Consumption: Efficient arc-on time and optimized motion paths lower power usage.
- Minimizing Waste: Higher first-pass yield rates reduce scrap.
- Enabling Lightweighting: Precision welding facilitates the use of advanced, thinner materials without compromising durability.
Looking ahead, AI-driven welding robots will leverage machine learning to self-optimize parameters for new materials, while collaborative robots (cobots) will assist operators in small-batch production.
Conclusion
In the high-stakes realm of automotive exhaust system manufacturing, welding robots—augmented by intelligent positioners and fixtures—represent the pinnacle of precision engineering. By automating complex welding tasks, these systems empower manufacturers to achieve faster cycle times, impeccable quality, and scalable production. As exhaust emission regulations tighten and vehicle designs evolve, robotic welding technology will remain a cornerstone of innovation, driving the automotive industry toward a smarter, cleaner future.
For industrial robot manufacturers, emphasizing these capabilities in exhaust pipe applications not only highlights technical expertise but also positions their solutions as essential partners in advancing automotive manufacturing excellence.
Post time: Mar-21-2025