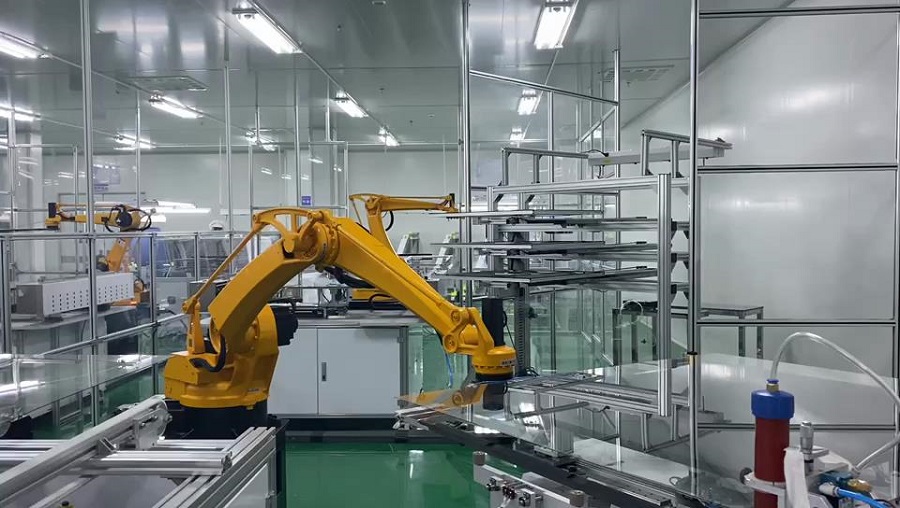
What is an industrial robot? What is it made of? How does it move? How do you control it? What does it do?
Maybe you are full of questions about the industry of industrial robots. These 9 knowledge points can help you quickly establish the basic understanding of industrial robots.
1. What is an industrial robot?
A robot is a machine with more degrees of freedom in three-dimensional space and can realize a lot of anthropomorphic actions and functions, and the industrial robot is used in the industrial production of robots. Its characteristics are programmable, anthropomorphic, universal, and mechatronics.
2. What are the systems of industrial robots? What does each do?
Drive system: The transmission that makes the robot work.
Mechanical structure system: a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical system composed of fuselage, arm, and tool at the end of a manipulator.
Sensing system: It is composed of an internal sensor module and an external sensor module to obtain information of internal and external environment status.
Robot-environment interactive system: The system that realizes the interaction and coordination between industrial robots and the equipment in the external environment.
Human-machine interaction system: operator participates in robot control and robot contact device.
Control system: According to the operation instruction program of the robot and the feedback signal from the sensor to control the robot's executive mechanism to complete the specified movement and function.
3. What is the meaning of robot freedom?
The degree of freedom refers to the number of independent coordinate axis movements of the robot, which should not include the opening and closing degree of freedom of the hand claw (end tool). In three-dimensional space, six degrees of freedom are needed to describe the position and attitude of an object, three degrees of freedom are needed for position operation (waist, shoulder, and elbow), and three degrees of freedom for attitude operation (pitch, yaw and roll).
Industrial robots are designed according to their purpose and may be less than or greater than six degrees of freedom.
4. What are the main parameters involved in industrial robots?
Degrees of freedom, repeated positioning accuracy, working range, maximum working speed, and carrying capacity.
5. What are the functions of the fuselage and the arm? What should we pay attention to?
The fuselage is a part of the supporting arm, which generally realizes the movement of lifting and pitching. The fuselage should be designed with sufficient stiffness and stability; The movement should be flexible, the length of the guide sleeve of the lifting movement should not be too short, to avoid the phenomenon of getting stuck, generally, there should be a guide device; The structure layout should be reasonable arm is the static and dynamic load of the wrist hand and the workpiece, especially when the high-speed movement will produce a large inertia force, cause impact, affect the accuracy of positioning.
When designing the arm, attention should be paid to high stiffness requirements, good steering, lightweight, smooth movement, and high positioning accuracy. Other transmission systems should be as short as possible to improve transmission accuracy and efficiency; The layout of each component should be reasonable, and the operation and maintenance should be convenient; Under special circumstances, the effect of thermal radiation should be considered in a high-temperature environment and the corrosion protection should be considered in a corrosive environment. A dangerous environment should consider riot control.
6. What is the primary function of the degree of freedom on the wrist?
The degree of freedom in the wrist is mainly about achieving the desired attitude of the hand. In order to make the hand can be in any direction of space, the wrist can realize the rotation of the three coordinate axes X, Y, and Z in space. That is, it has three degrees of freedom, flipping pitch, and deflection.
7. Functions and characteristics of the end tools of the robot
A robotic hand is a component used to hold a workpiece or a tool. It is a separate component that can have a claw or a special tool.
8. According to the clamping principle, which types of end tools are divided into? What specific forms are included?
According to the clamping principle, the end clamping hand is divided into two categories: the clamping class includes internal support type, external clamping type, translation external clamping type, hook type, and spring type; The adsorption class includes the magnetic suction type and air suction type.
9. The difference between hydraulic and pneumatic transmission in operating force, transmission performance, and control performance?
Operating power. Hydraulic can get great linear motion and rotary force, grab the weight of 1000 to 8000N; The air pressure can get small linear motion force and rotary force, and grab weight is less than 300N.
Transmission performance. Hydraulic compressibility is small transmission smooth, no impact, basically, no transmission lag phenomenon, reflecting sensitive movement speed up to 2m/s; The pressure compressed air viscosity is small, the pipeline loss is small, the flow rate is large, the speed is high, but the stability is poor at high speed, the impact is serious. Usually, the cylinder is 50 to 500mm/s.
Control performance. Hydraulic pressure and flow are easy to control, stepless speed regulation through regulation; Low pressure is not easy to control, difficult to accurately locate, and generally does not do servo control.

Post time: Dec-07-2022




