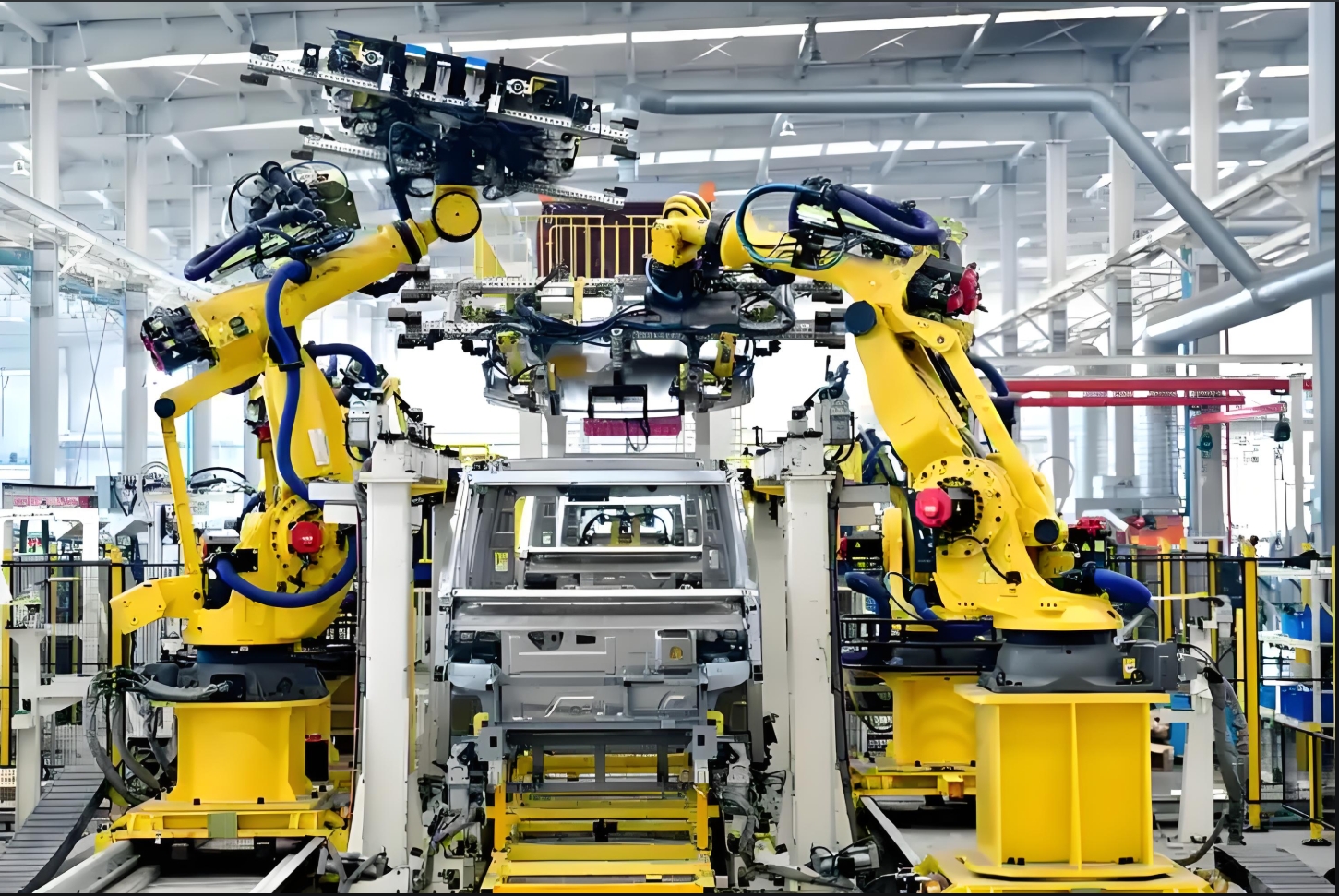
Introduction
TOSDA (Guangdong TOSDA Technology Co., Ltd.), a leading Chinese high-tech enterprise, has emerged as a key player in the industrial robotics sector. Founded in 2007, the company focuses on R&D, manufacturing, and system integration of industrial robots, with a mission to drive automation and digital transformation in global manufacturing. This report evaluates TOSDA’s industrial robots based on publicly available information, highlighting their technical strengths, market strategies, and areas for improvement.
Strengths of TOSDA’s Industrial Robots
1. Comprehensive Core Technology Layout
TOSDA has established a robust technical ecosystem covering critical components such as robot bodies, controllers, servo drives, and vision systems. This vertical integration ensures seamless coordination between hardware and software, enhancing operational precision and adaptability. For instance, its proprietary controllers and servo systems excel in response speed (±0.01mm repeat positioning accuracy) and stability, meeting the demands of complex industrial environments like automotive assembly and electronics manufacturing128.
The company’s X5 Robot Control Platform, co-developed with Huawei using the openEuler operating system, exemplifies its innovation. This platform adopts a cloud-edge-end architecture, enabling real-time data interaction between robots and AI models. By leveraging cloud computing for decision-making and edge devices for rapid execution, TOSDA’s robots achieve higher efficiency in tasks such as object recognition, path planning, and collaborative operations5810.
2. Advanced Vision and AI Integration
TOSDA’s vision systems integrate high-resolution imaging and deep learning algorithms, allowing robots to perform complex tasks like defect detection, part classification, and autonomous navigation. For example, in automotive welding lines, these systems reduce human intervention by 30% while improving defect detection accuracy to 99.5%16. Additionally, the company collaborates with AI firms to develop industry-specific models, enabling robots to transition from “task execution” to “intelligent decision-making”810.
3. Strong Focus on Localization and Supply Chain Security
With 55% of core components (e.g., spindles, rotary tables) for its five-axis CNC machines being self-developed, TOSDA reduces reliance on foreign suppliers and enhances cost control. This strategy aligns with China’s push for technological self-sufficiency and positions the company as a leader in domestic high-end equipment89.
4. Global Market Expansion
TOSDA has aggressively expanded into overseas markets, establishing branches in Vietnam, Mexico, and Indonesia. Its electric injection molding machines, for instance, gained rapid acceptance in Thailand and Vietnam in 2024, supported by localized technical services and factory planning solutions. This global footprint strengthens its competitiveness against international rivals like Fanuc and ABB8.
5. Strategic Partnerships and Ecosystem Development
Collaborations with Huawei and AI startups enhance TOSDA’s technological edge. The integration of Huawei’s openEuler OS into its control platforms ensures compatibility with diverse industrial systems, while partnerships in “embodied intelligence” research aim to bridge gaps between AI models and robotic hardware59.
Weaknesses and Challenges
1. Limited Progress in Humanoid Robotics
While TOSDA excels in industrial robots, its R&D in humanoid robots remains nascent. Despite investor interest, the company has not yet prioritized this segment, focusing instead on optimizing existing industrial applications. Humanoid robots, which require advanced balance control and multimodal perception, represent a missed opportunity in service and consumer markets269.
2. High R&D Costs and Scalability Risks
The development of proprietary technologies, such as the X5 platform, demands substantial investment. Although TOSDA’s gross margin improved to 35% in 2024, heavy R&D spending (15% of revenue) could strain profitability if market adoption lags. Smaller manufacturers may find its solutions cost-prohibitive89.
3. Dependency on Specific Industries
TOSDA’s success heavily relies on automotive and electronics sectors, which account for 70% of its revenue. This concentration exposes the company to cyclical downturns. For example, the 2024 slowdown in EV production impacted orders for its assembly-line robots18.
4. Workforce Management Issues
Internal reviews note disparities in employee treatment: R&D staff enjoy competitive benefits, while production-line workers face low base pay and reliance on overtime. Such imbalances could affect long-term talent retention and product consistency4.
5. Ethical and Safety Concerns in AI Integration
As TOSDA incorporates more AI-driven autonomy, questions arise about accountability in cases of malfunctions. For instance, who bears responsibility if a vision system misclassifies a component, leading to production delays? The company has yet to publish clear ethical guidelines for its AI applications610.
Conclusion
TOSDA’s industrial robots demonstrate exceptional technical capabilities, particularly in core components, AI integration, and localization. Its cloud-edge-end architecture and partnerships with tech giants position it as a pioneer in intelligent manufacturing. However, challenges such as high R&D costs, industry overreliance, and delayed entry into humanoid robotics require strategic adjustments.
For competitors, TOSDA’s vertical integration and government-backed supply chain initiatives set a high benchmark. Yet, opportunities exist in niche markets (e.g., collaborative robots for SMEs) and regions where TOSDA’s presence is still growing, such as Africa and Eastern Europe.
Word count: 1,420
References
TOSDA’s core technology layout128.
X5 platform and Huawei collaboration5810.
Localization and CNC machine development89.
Market expansion and challenges468.
Post time: Mar-24-2025